Yes, optical fibers have become increasingly important in various industries, including military and aerospace. A recent report by MarketsandMarkets states that the “Fiber Optic Cables Market for Military & Aerospace is projected to reach USD 1.5 billion by 2026,” with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% throughout the forecast period. The market growth is attributed to various factors, including the emergence of fiber optics-based avionics systems, an increasing requirement for fiber optic cables in aircraft interiors, and the development of spacecraft designs based on fiber optics technology.
Additionally, fiber optics can be used in military aircraft and spacecraft designs to enable faster and more reliable data transmission, which can improve system performance and reduce the risk of failure. With the growing optical fiber use cases in defence, these technologies will likely continue to play an increasingly important role in providing the necessary infrastructure to support the requirements of military troops.
What challenges led to the adoption of optical fiber technology in defence:
The defence began using optical fiber in their processes to address several challenges they were facing with conventional technology, including radio wave and microwave-based transmission systems. Some of them are as follows:
High Attenuation and Low Bandwidth:
One of the main challenges was the need for a high-speed and reliable communication network that could transmit large amounts of data quickly and securely. The traditional copper cable networks that were previously used had limitations in terms of bandwidth and distance, which made them inadequate for meeting the defence's communication needs.
Eavesdropping:
Another challenge was the need for secure and protected communication channels that could not be intercepted or compromised by unauthorized individuals or entities. In addition to its secure form of data transmission, optical fiber technology can be deployed with enhanced security features such as encryption, which significantly reduces the risk of interception or hacking.
Network Deployment Challenges in Harsh Environments:
The defence also needed to deploy communication networks in remote and harsh environments, which made the installation and maintenance of traditional cable networks challenging. Optical fiber technology allows for easier and more cost-effective deployment in such environments due to its lightweight and flexible design.
Optical fiber technology has enabled the defence to enhance their communication capabilities, boost data transfer speeds, safeguard sensitive information, and deploy networks more effectively in harsh and remote environments.
.png)
Applications of optical fiber in defence
Major optical fiber use cases in defence:
There are certain optical fiber use cases in defence due to their property of being less susceptible to battle damage than conventional electrical cabling systems.
For instance, large electrical pulses can be generated in wires and cables by electromagnetic fields due to nuclear weapon detonations, lightning strikes, and other factors. These pulses can disrupt the functionalities of internal electronics and even result in the damage of components if they have enough energy. However, optical fibers and their interfaces are not affected by electromagnetic pulses, making fiber-optic interconnects an ideal solution for maintaining electromagnetic pulse immunity. To further improve the ability to survive battle damage, a redundant fiber-optic interconnect system can be implemented, which is practical due to the lighter weight of fiber optics compared to traditional systems. Additionally, optical fibers can withstand higher temperatures, reducing the risk of sparks and shorts in hazardous areas.
Let’s have a look at other use cases of optical fiber in the defence:
Enhanced and Secured Communication:
Fiber optics are considered a highly secure means of communication for military applications due to their unique characteristics. Unlike traditional copper wires, fiber optics use light to transmit data, which means that no electromagnetic fields are produced during the transmission. This makes it extremely difficult for an eavesdropper to intercept or tap into the communication signal.
The lack of electromagnetic emissions from fiber optics also makes them immune to interference from radio frequency (RF) devices, which are commonly used for wireless communication. This eliminates the risk of jamming or other forms of interference that can disrupt military communication systems. The use of fiber in communication systems enables longer transmission distances without the need for repeaters compared to twisted copper wires or coaxial cables. Rigorous testing conducted by all three military services has indicated that under most battlefield conditions, optical fiber systems exhibit superiority.
Weaponry:
Fiber optic technology is finding new use cases in defence weapons as the need for better communication and precision guidance increases. The FOG-M and FOG-S weapons, which use fiber optic cables are hit-to-kill weapons designed to take down helicopters, ground vehicles, and tanks. The use of fiber optic cables enables a high bandwidth data link, which is not possible with traditional copper cables. This link provides better communication between the missile and the gunner, allowing the missile to be guided more precisely to its target.
Another optical fiber use case in defence that is being considered by the Army is the PDAMS ballistic missile bus system, which carries submunitions linked to the bus by fiber optic cables. This system would be used to destroy tactical ballistic missiles within minutes of hostilities. The Air Force and Navy are also considering fiber-guided weapons that can be dispensed from an aircraft. The development of these fiber optic-guided weapons represents a significant advancement in defence technology, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of military operations.
Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR) Systems:
Among the various types of sensors used in ISR, those that rely on optical technology are a major component of modern ISR systems. Specialty optics, such as night vision goggles, helmet recording camera systems, thermal imaging sights, and spotting scopes, play a crucial role in the success of soldiers on the ground. The optics in these units are designed to be durable and reliable, even in extreme conditions. They are typically made of lightweight, rugged materials that can withstand the impacts of water and dust.
Optical sensors are particularly useful in ISR operations because they can provide high-resolution imagery over large areas, even from considerable distances. This enables analysts to collect detailed information about potential targets, including their location, movement patterns, and even their composition. As technology continues to advance, the use of optical sensors in ISR is likely to become even more prevalent.
Navigation:
Fiber Optic Gyroscopes (FOGs) are crucial in the military due to their exceptional performance in measuring angular rate and acceleration in addition to their superior dynamic range and reliability. They have a vast range of applications in military vehicles such as tanks, self-propelled artillery, submarines, and armored assault vehicles. In situations where electronic interference hinders satellite navigation's accuracy, FOGs can be used to enable autonomous navigation, precise guidance, and accurate target hitting for aircraft.
Moreover, FOGs are critical components in aviation fire control systems, providing stability to aiming and firing lines of weapon systems, such as armed helicopters. This capability ensures that weapons can perform search, aim, track, and shoot in motion accurately. FOGs are also the only navigation technology that works effectively underwater, making them crucial for the positioning, orientation, and navigation of submarines.
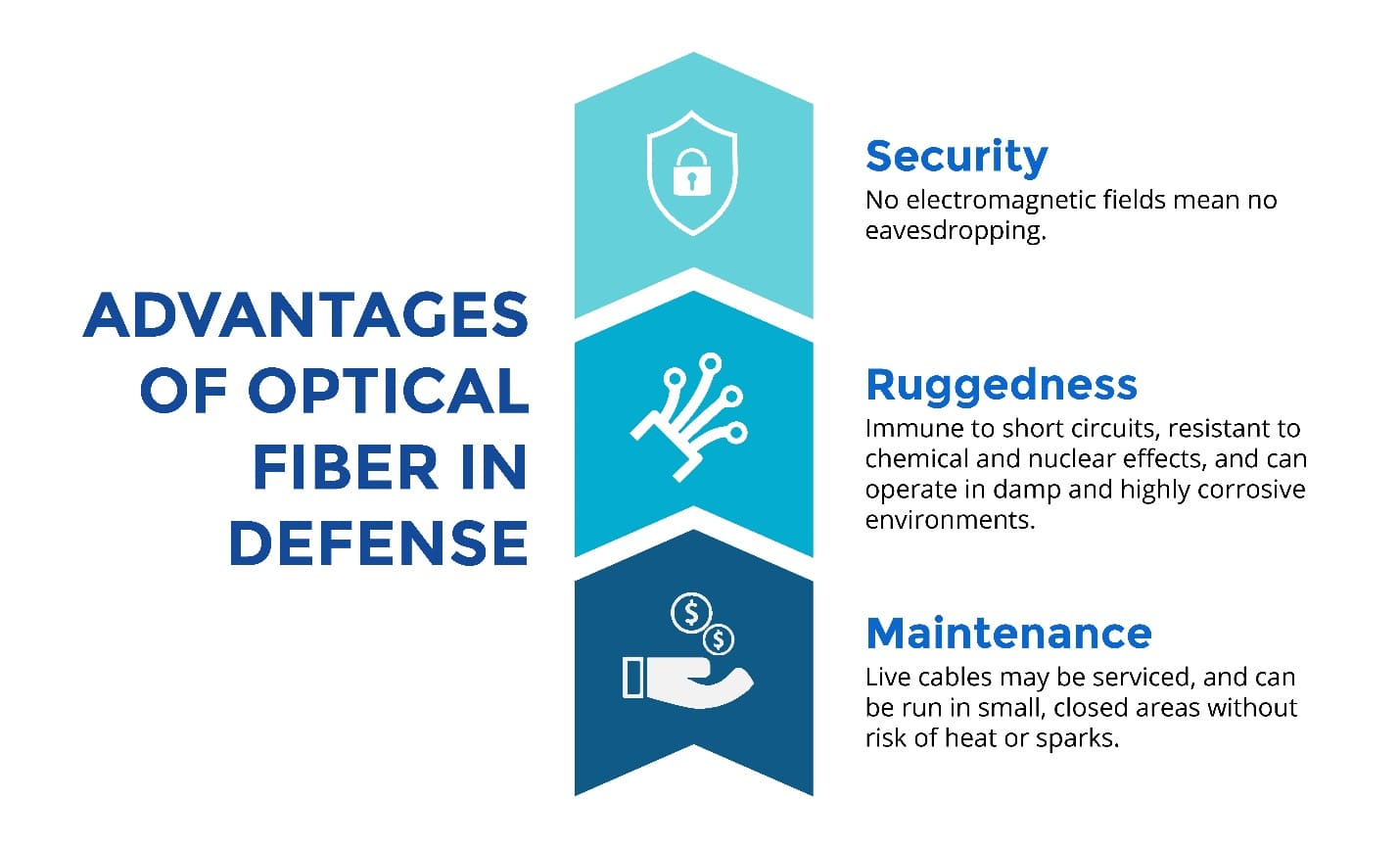
Advantages of optical fiber in defence
Avionics:
Fiber optics technology is revolutionizing avionics in defence by providing solutions to size, weight, and power (SWaP) challenges while enabling high-speed processing and data transmission. Military fighter aircraft, for instance, requires a high-speed operation to detect targets and incoming missiles. With fiber-optic-based systems, avionics can deliver real-time imaging without digital or video compression. This capability supports quick, decisive actions by pilots based on radar and camera images, which is critical in combat situations. Additionally, the next-generation military fighter platforms will require extremely high data transmission speeds with low latency, which fiber optics networks can deliver. Although the development of fully autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) is still in its early stages, the high-speed capability of fiber optics networks will bring this technology closer to realization. The use of fiber optics in avionics is a game-changer, enabling next-generation avionics systems to meet the demanding requirements of modern defence missions.
Others:
Optical fibers are also used in other defence applications such as acoustic sensing, chemical sensing, and laser systems. The fibers are used for remote sensing of underwater objects and for detecting chemical agents in the air. They are also used in laser-based weapons systems for transmitting high-energy laser beams.
Final Words:
In summary, the use of optical fiber in the defence sector has proved to be a game-changer for military operations worldwide. Its high-speed, secure, and reliable transmission capabilities have enhanced communication capabilities and improved overall situational awareness, enabling military personnel to make more informed decisions and respond more quickly to changing situations. With the demand for communication systems increasing, the application segment of fiber optic cables is expected to see significant growth in the military and aerospace market.
Furthermore, the Asia Pacific region is expected to lead this market in the coming years, driven by growing economies like India and China, extensive R&D activities, increasing funding and investments in defence products, and favorable regulatory policies.