Fiber Optics is an optical communications technology that allows for the transmission of data over long distances without any loss of information. This technology was originally developed to allow telephone communication over longer distances using a single ground wire and an optical fiber, which made it far more cost-effective than systems based on repeaters or multiple copper lines. Optical fiber cable allows the delivery of data, voice, video and any other type of signal to be sent through glass or plastic fibers. Optical cables are made out of flexible and light materials that protect the optical fibers inside from tension, bending, or crushing without impacting the ability of the fibers to transmit signals.

How optical fibers work?
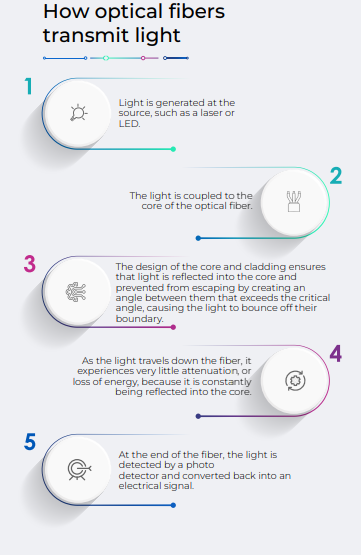
Let’s now understand how signal transmission over optical
fiber works. The
process begins with a transmitter, which converts electrical signals into light signals.
These light
signals are launched into the core of the optical fiber, which is surrounded by a
cladding layer. The
core is typically made of glass or plastic and is designed to carry the light signal.
The cladding layer
is made of a different type of glass or plastic and serves two functions. First, the
cladding is
designed to reflect light back into the core, helping to maintain signal power. Second,
the cladding
provides physical protection for the core.
As the light travels through the core of
the optical
fiber, it bounces off the cladding layer at a shallow angle. The design of the core and
cladding ensures
the light undergoes total internal reflection, keeping the light within the core. The
light signal can
travel for very long distances with minimal attenuation (loss of signal strength) as
long as the fiber
is kept free from damage or attenuation-causing factors such as bending, contamination,
or attenuation
due to atmospheric conditions.
The signal is then received at the other end by a
receiver, which
converts the light signal back into an electrical signal. This signal can be sent over
very long
distances without significant loss of signal strength, and it is also less susceptible
to interference
than other types of communication cables. Fiber
optical cable is widely used for long-distance communication, including internet
connectivity,
telephone lines, and cable television transmission, due to its high bandwidth and low
attenuation
characteristics.
Major Applications for Fiber Optic Cable:
The following is a brief look at some different applications for fiber optic cable:
Technology has revolutionized communications, and it continues to do so today. Fiber
optics may be
found in the world of modern-day manufacturing, but they can also be found within your
home or office.
If you're curious about fiber optic cable, keep reading!
Telecommunication:
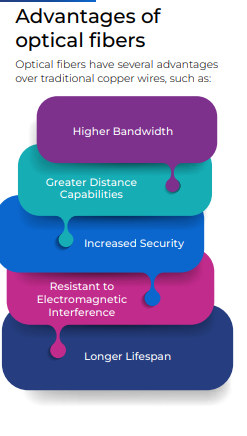
Fiber optics are one of the most versatile and consistent systems that have been developed to date. One of the main applications of fiber optics is broadband communications due to their high transmission capacity and low interference. This can be applied not only for long-distance links but also for local networks within a particular area, which allow faster transmission speed compared to copper-based systems. The use of fiber optics has also improved the reliability and security of telecommunications networks, as fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference and difficult to tap into without detection. Fiber optic cables can transmit data at high speeds thus, making them the preferred choice for high-speed internet, cable TV, and telephone services.
Aerospace and Defence:
Optical fiber has several uses in military and aerospace applications due to its unique properties of high bandwidth, low attenuation, and immunity to electromagnetic interference. The use of optical fibers in communication systems ensures high-speed and secure transmission, making it difficult for the enemy to intercept or jam the signal. Fiber optic sensors are used in aircraft engines, weapons systems, and other critical components to monitor their performance and detect any faults or malfunctions. Optical fibers in military and aerospace applications have revolutionized communication, sensing, and weapons systems, providing high-speed and reliable connectivity in harsh and challenging environments.
Networking:
Fiber optics has become an essential part of modern networking infrastructure because it offers several advantages over traditional copper-based cables, including higher bandwidth, longer transmission distances, and improved reliability. This technology is commonly used for long-distance communication, such as transcontinental communication. Many internet service providers (ISPs) use fiber optics to deliver high-speed internet to homes and businesses. Fiber optic cables can transmit data at speeds of up to 800 Gbps , making it ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications like video streaming and online gaming. Fiber optics is also commonly used in data centers to connect servers, storage devices, and other networking equipment. This is because optical fiber cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, making them more reliable and secure than traditional copper-based cables
Where can you find the best quality optical fibers?
There are several companies that specialize in manufacturing high-quality optical fibers, and HFCL is among them. HFCL produces optical fiber cables that are sturdy, long-lasting, have a high bandwidth capacity, and require minimal upkeep. The company is specialized in manufacturing various types of optical fibers and cables that are of superior quality, such as Flexi Bend, Flexi Arch, Flexi Arch Plus, and Low Attenuation Loss Fiber. These fibers can be used in a variety of applications, including long-distance transmission, metro networks, access networks, broadband networks, and others.
Final Words
Fiber optics is the backbone of modern life. It enables the communication between computers, cell phones, and other electronic devices that use light signals to transmit data. The use of fiber optic cable is not limited to the office or home. They are also being used in various industries for enhanced communication, performance, and connectivity. Overall, fiber optics has revolutionized the way we communicate and access information, and it will continue to play a critical role in the development of modern networking infrastructure.